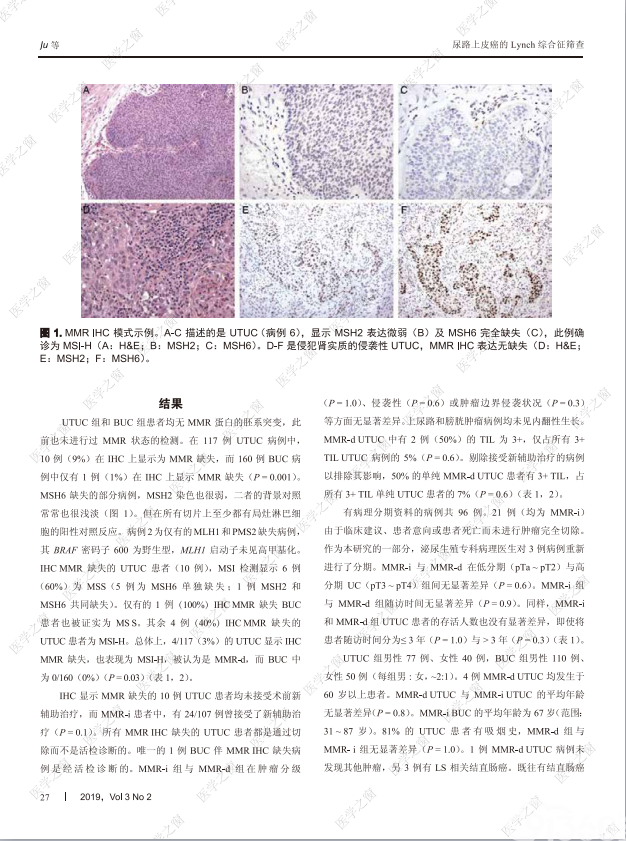
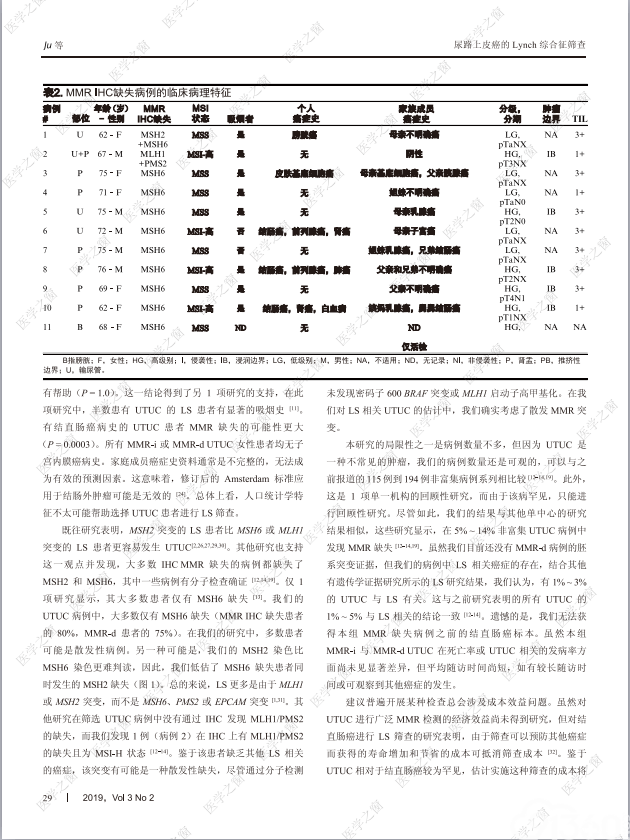
摘要:Lynch综合征(lynch syndrome, LS)的特征是DNA错配修复(mismatch repair, MMR)基因的胚系突变,受累患者具有患多种癌症的高风险。尽管上尿路的尿路上皮癌(upper tract urothelial carcinoma, UTUC)是LS患者第三常见的恶性肿瘤,但目前仅对结直肠癌和子宫内膜癌推荐应用免疫组织化学(immunohistochemistry, IHC)检测 MMR 蛋白缺失。为了探究在UTUC患者中普遍进行MMR IHC筛查是否适宜,我们以膀胱尿路上皮癌(bladder urothelial cardnoma, BUC)为对比,研究了 MMR在UTUC中的表达和微卫星状态,并对UTUC的临床病理特征进行了评估。我们发现,9%的UTUC显示MMR IHC缺失(8例仅有MSH6缺失;1例为MSH2和MSH6缺失;1例为MLH1和PMS2缺失;n = 117),而BUC的缺失率仅有1%(仅1例MSH6缺失;n = 160)(p = 0.001)。在这些病例中,分子检测显示,4/10 (40%)的UTUC存在微卫星高度不稳定性(占全部UTUC的3%; 3例仅有MSH6缺失;1例为MLH1和PMS2缺失),而BUC中无1例检测出微卫星高度不稳定性(P = 0.03)。预测由MMR缺失的唯一临床病理特征是患者既往结直肠癌病史(p=0.0003)。然而,LS患者发生UTUC和结肠癌的发病年龄相似,因此,UTUC可能是某些LS患者的首发肿瘤(前哨事件)。将我们的结果与其他研究结合显示,1% ~ 3%的UTUC病例可能是LS相关癌。2% ~ 6%的结直肠癌和子宫内膜癌病例与LS相关。LS在UTUC中的实际比例可能与之类似,因此我们建议,诊断指南应推荐对所有UTUC进行MMR IHC筛查和微卫星不稳定性检测。
关键词:上尿路,尿路上皮,Lynch综合征,错配修复,微卫星不稳定性
(Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1549-1555)
美国外科病理学杂志中文版2019年第2期全文No.4
(侯 静/郑林茂 翻译 周 桥 审校)





The American Journal of Surgical Pathology中文版声明:
©2018 Wolters Kluwer Health
The material is published by Wolters Kluwer Health with the permission of American Journal of Surgical Pathology.No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form,stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form,by any means,without prior written permission from Wolters Kluwer Health.Opinions expressed by the authors and advertisers are not necessarily those of the American Journal of Surgical Pathology, its affiliates,or of the Publisher.The American Journal of Surgical Pathology,its affiliates,and the Publisher disclaim any liability to any party for the accuracy,completeness,efficacy,or availability of the material contained in this publication (including drug dosages) or for any damages arising out of the use or non-use of any of the material contained in this publication.
Although advertising material is expected to conform to ethical (medical) standards,inclusion in this publication does not constitute a guarantee or endorsement of the quality or value of such product or of the claims made of it by its manufacturer.




 苏公网安备 32011402011742
苏公网安备 32011402011742